This can be understood most easily by thinking of a series of shortrun average total cost curves, each one for a different level of the fixed input, capital, as shown in Figure 1 Figure 1 The LongRun Average Cost Curve as the Lower Boundary of
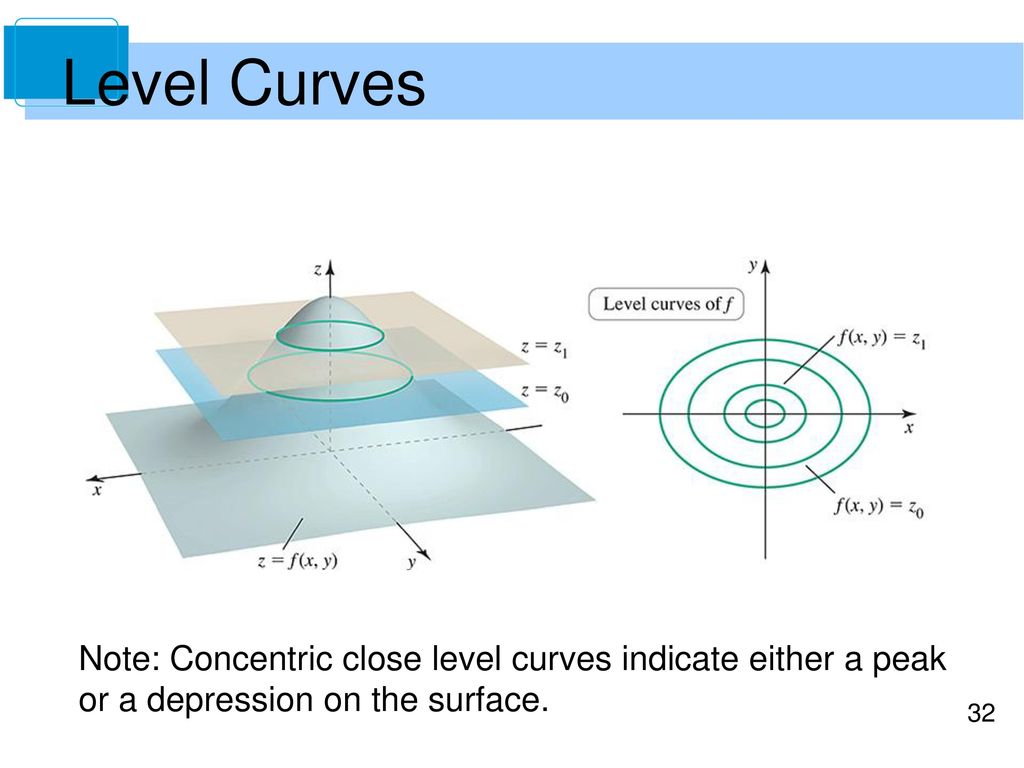
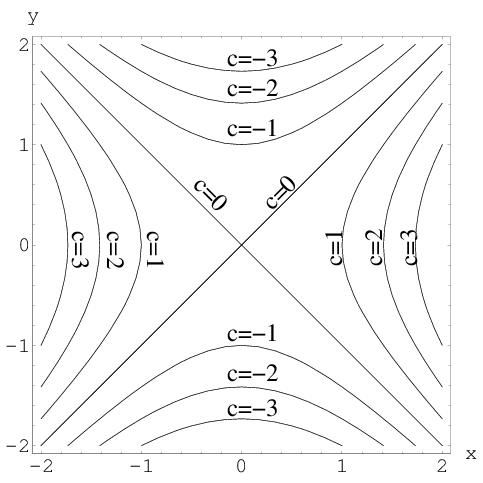
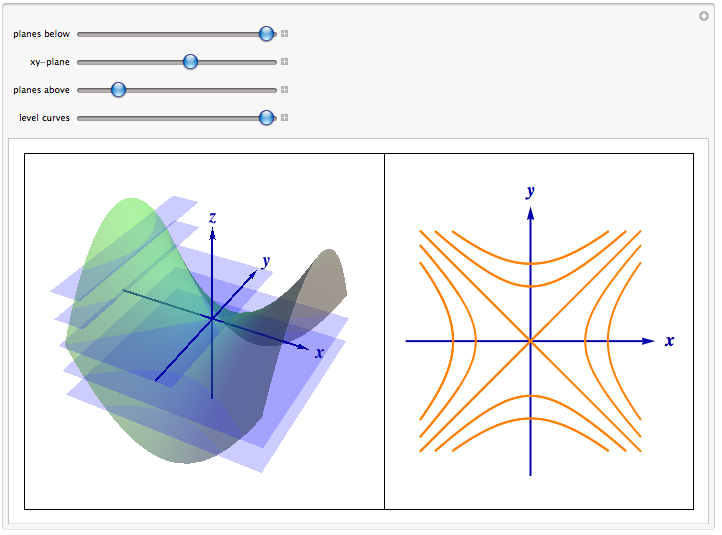
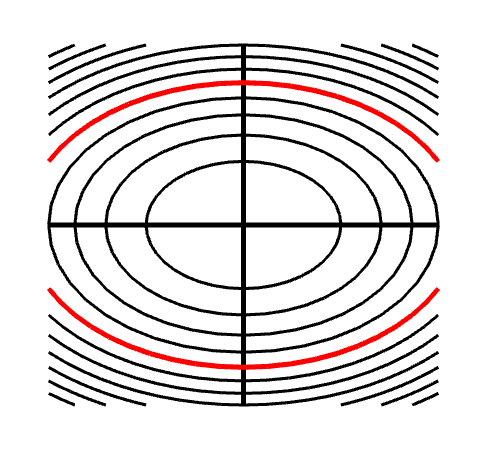
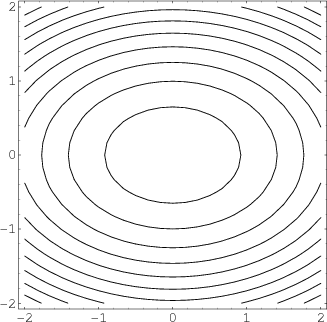
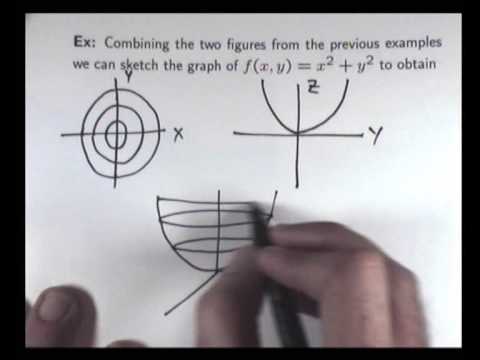
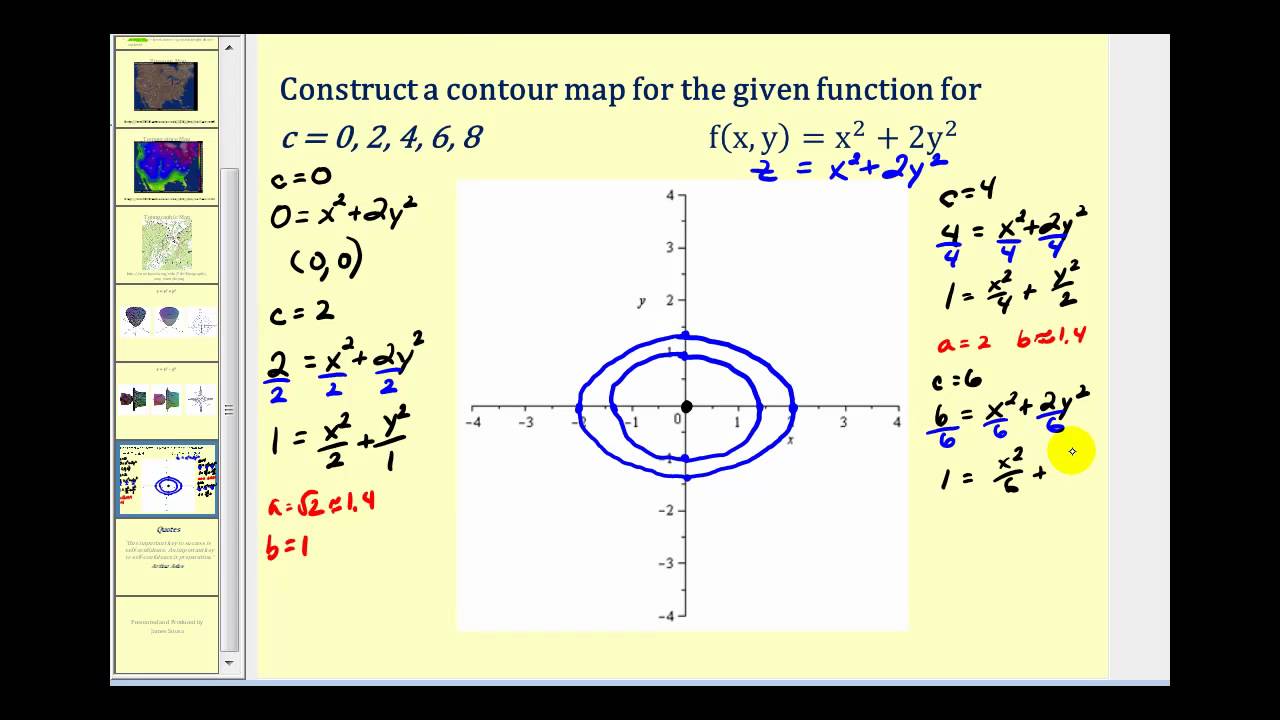
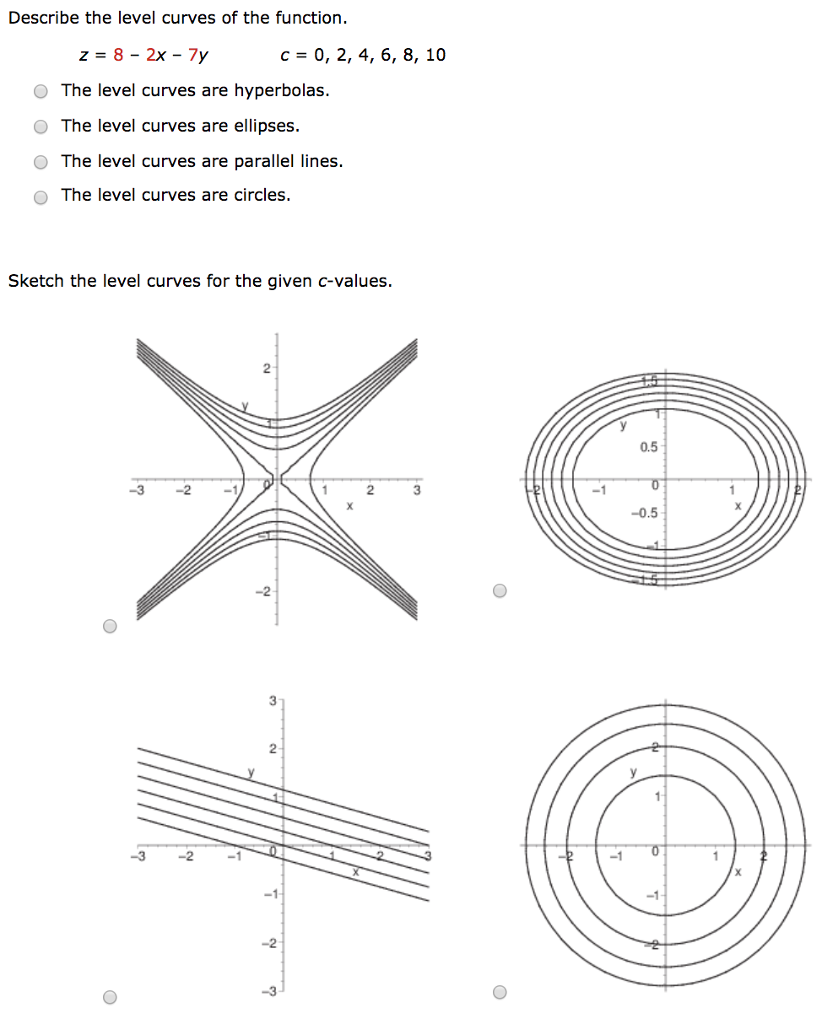
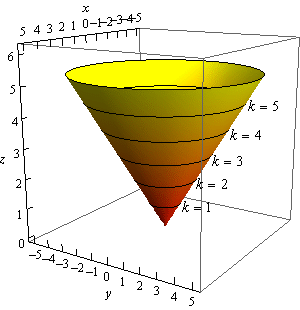
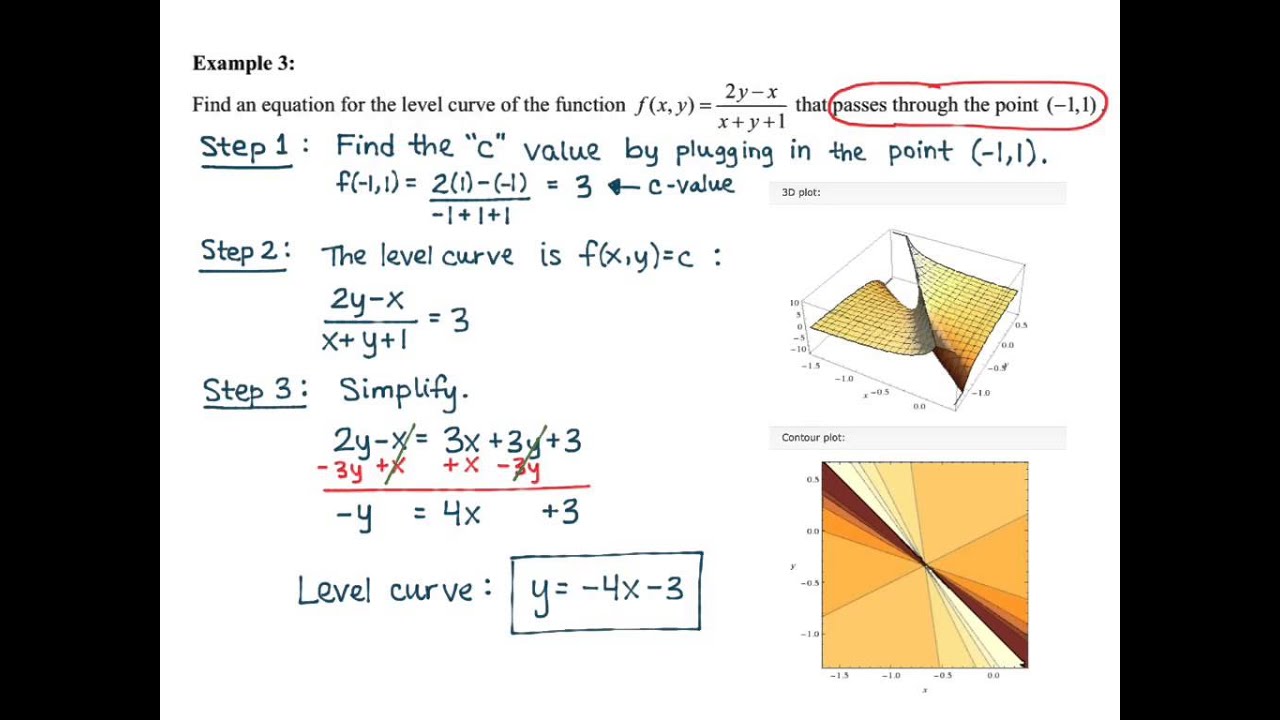
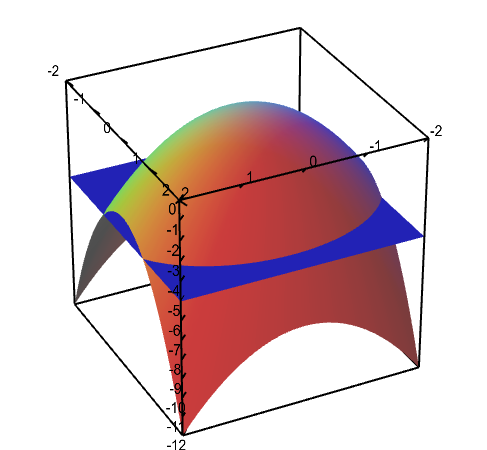
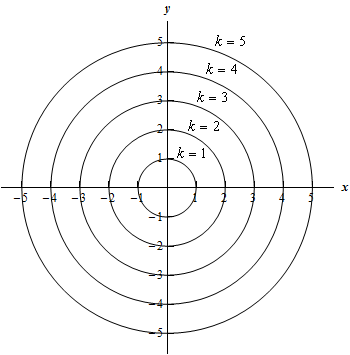
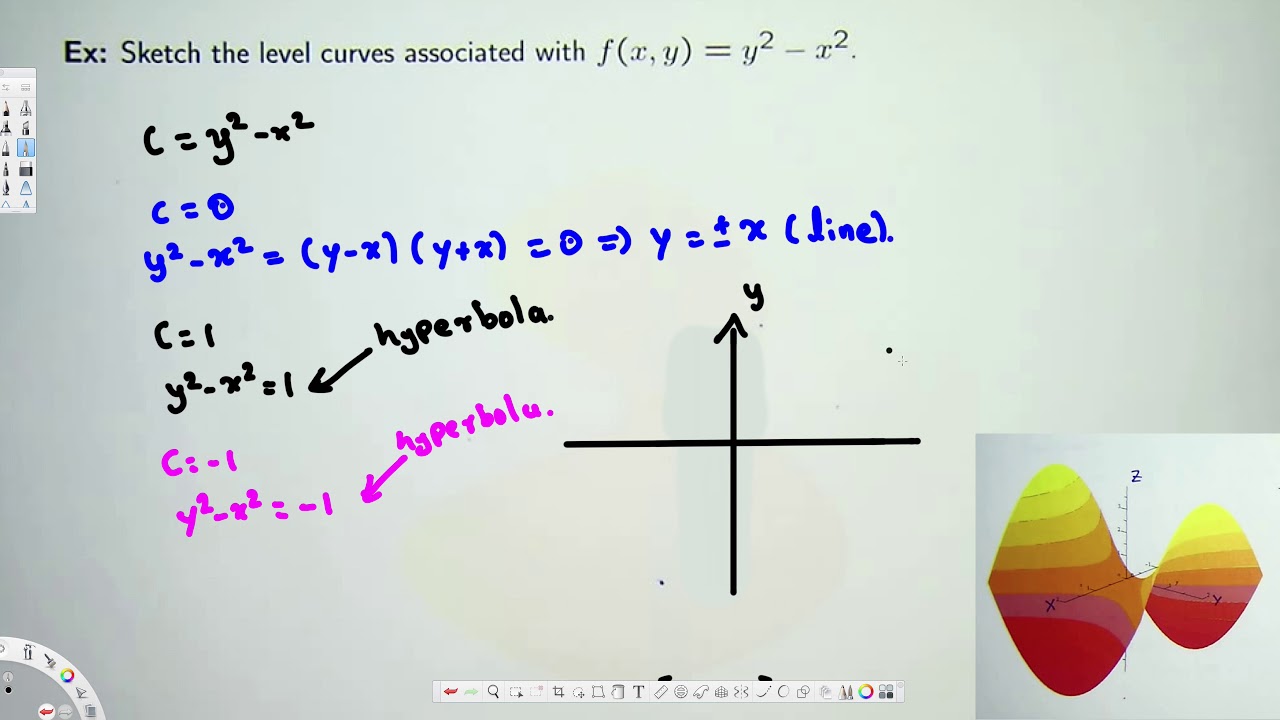
How to determine level curves-ContourPlot is also known as an isoline, isocurve, level set or sublevel set When given a function f, ContourPlot constructs contour curves corresponding to the level sets where f x, y has constant values c 1, c 2, etc By default, the regions between the curves are shaded to more easily identify regions whose values are between c i and c i 1Level Curves Example 1 (Solution Strategy) Sketch some level curves of the function Solution First, let z be equal to k, to get f (x,y) = k Secondly, we get the level curves, or
How to determine level curvesのギャラリー
各画像をクリックすると、ダウンロードまたは拡大表示できます
 | ||
 |  | |
 |  | |
 | ||
「How to determine level curves」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  | |
「How to determine level curves」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  | |
 |  | |
 |  | |
「How to determine level curves」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 |  |  |
 |  | |
 |  | |
「How to determine level curves」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 |  | |
 | ||
 |  |  |
「How to determine level curves」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
「How to determine level curves」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  | |
 |  |  |
「How to determine level curves」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 | ||
 |  | |
 |  |  |
 |  | |
「How to determine level curves」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 | ||
 |  | |
 |  |
Normal distributions become more apparent (ie perfect) the finer the level of measurement and the larger the sample from a population You can also calculate coefficients which tell us about the size of the distribution tails in relation to the bump inCurves in R2 Graphs vs Level Sets Graphs (y= f(x)) The graph of f R !R is f(x;y) 2R2 jy= f(x)g Example When we say \the curve y= x2," we really mean \The graph of the function f(x) = x2"That is, we mean the set f(x;y) 2R2 jy= x2g Level Sets (F(x;y) = c) The level set of F R2!R at height cis f(x;y) 2R2 jF(x;y) = cg Example When we say \the curve x 2 y = 1," we really mean
Incoming Term: level curves examples, how to describe level curves, how to determine level curves, how to do level curves,




0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿